Currently Empty: $0.00


How to Start a Career in Tech: A Clear Guide for Beginners
Breaking into tech can feel confusing when you do not know where to begin or which path fits you. This guide explains the major tech career options, what they actually involve, and how to take your first practical steps with clarity and confidence, even if you have no prior experience.
A clear view of tech career path
Understand the difference between technical and non-technical roles and identify which path fits your interests.
The best place to start your Journey
Learn where beginners should begin, which skills matter early, and how to avoid common entry-level mistakes.
A practical roadmap to move forward
By the end of the page, you will know what steps to take next, learning a skill?, choosing a course?, or building experience.
Introduction to Careers in Tech
Starting a career in tech can feel confusing, not because of a lack of opportunity, but because there are so many paths to choose from. From software development and cybersecurity to product management, design, and writing, beginners often struggle most with knowing where to start and what role fits them.
Tech careers are not limited to coding roles alone. The industry is built on both technical and non-technical positions, each requiring different skills and learning approaches. This guide breaks these options into two clear paths to help you understand where you fit and how to take your first practical steps into tech.
- Technical Path
- Non Technical Path
The technical path focuses on building and maintaining technology systems and products. These roles involve working directly with software, data, infrastructure, or security, and typically require learning specific tools and technical concepts. Common roles include software development, web and mobile development, data analysis, cybersecurity, cloud engineering, and quality assurance testing.
While the learning curve can feel steep at first, technical roles reward consistency and hands-on practice. Many beginners enter this path through structured learning, practical projects, and continuous skill development rather than formal degrees. This path is well suited for people who enjoy problem-solving, logical thinking, and building solutions that work at scale.
The non-technical path focuses on shaping, supporting, and scaling technology products without requiring deep coding skills. These roles exist across product management, design, marketing, technical writing, customer success, operations, and project coordination, and they play a critical role in how tech products are planned, communicated, and delivered.
Although these roles do not involve heavy programming, they still require a solid understanding of how technology works at a high level. Strong communication, research, organization, and strategic thinking are essential. This path is ideal for people who enjoy working with users, teams, and ideas rather than building software directly.


Technical Courses
Pick A Technical Course To Get Started
All Levels
$38.00 Original price was: $38.00.$12.54Current price is: $12.54.
HTML, CSS, and Javascript Course for Web Developers
(5.0/ 1 Rating)
- 100 Lessons
- 1301 Students
All Levels
$38.00 Original price was: $38.00.$12.54Current price is: $12.54.
HTML, CSS, and Javascript Course for Web Developers
(5.0/ 1 Rating)
Have you been on the hunt looking to add to your existing skills? Congratulations, your search ends here! This is...
- 100 Lessons
- 1301 Students
All Levels
$47.50 Original price was: $47.50.$9.50Current price is: $9.50.
Cross Platform Android, iOS and Web App Development
(5.0/ 6 Ratings)
- 21 Lessons
- 49 Students
All Levels
$47.50 Original price was: $47.50.$9.50Current price is: $9.50.
Cross Platform Android, iOS and Web App Development
(5.0/ 6 Ratings)
Are you looking to create awesome, cross-platform mobile apps without the stress of learning how to code? Look no further....
- 21 Lessons
- 49 Students
Intermediate
$36.10 Original price was: $36.10.$11.40Current price is: $11.40.
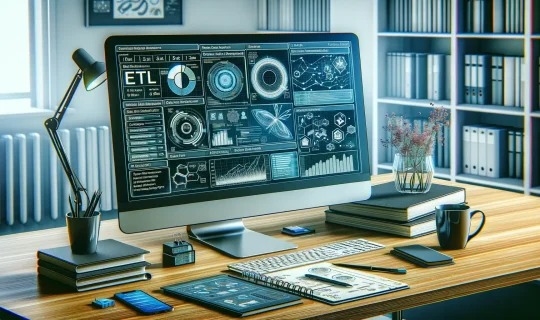
ETL, Data Preparation and Data Cleaning with Power Query
(0.0/ 0 Rating)
- 41 Lessons
- 15 Students
Intermediate
$36.10 Original price was: $36.10.$11.40Current price is: $11.40.
ETL, Data Preparation and Data Cleaning with Power Query
(0.0/ 0 Rating)
If you work with data in any capacity, you probably know that the most tedious part of all the tasks...
- 41 Lessons
- 15 Students
Beginner
$32.30 Original price was: $32.30.$5.70Current price is: $5.70.
aptLearn Cyber Security Certification Course
(0.0/ 0 Rating)
- 66 Lessons
- 247 Students
Beginner
$32.30 Original price was: $32.30.$5.70Current price is: $5.70.
aptLearn Cyber Security Certification Course
(0.0/ 0 Rating)
Welcome to our comprehensive Cyber Security course! This course is designed to provide a complete understanding of Cyber Security, from...
- 66 Lessons
- 247 Students
Intermediate
$36.10 Original price was: $36.10.$9.50Current price is: $9.50.
Data Analysis and Visualization Course
(0.0/ 0 Rating)
- 61 Lessons
- 82 Students
Intermediate
$36.10 Original price was: $36.10.$9.50Current price is: $9.50.
Data Analysis and Visualization Course
(0.0/ 0 Rating)
Are you ready to unlock a fast track to career advancement with one game-changing skill? Welcome to the empowering world...
- 61 Lessons
- 82 Students
Beginner
$28.50 Original price was: $28.50.$7.60Current price is: $7.60.
Full Course on Microsoft Excel Basics Extra
(0.0/ 0 Rating)
- 58 Lessons
- 47 Students
Beginner
$28.50 Original price was: $28.50.$7.60Current price is: $7.60.
Full Course on Microsoft Excel Basics Extra
(0.0/ 0 Rating)
Microsoft Excel is the most used software in the world and possibly beyond (I have a hunch that Angels use...
- 58 Lessons
- 47 Students
Intermediate
$38.00 Original price was: $38.00.$9.50Current price is: $9.50.
Project Management Certification in Software Engineering
(0.0/ 0 Rating)
- 148 Lessons
- 30 Students
Intermediate
$38.00 Original price was: $38.00.$9.50Current price is: $9.50.
Project Management Certification in Software Engineering
(0.0/ 0 Rating)
Welcome to the Project Management Course! Whether you're new to managing projects or looking to enhance your skills, this course...
- 148 Lessons
- 30 Students
Intermediate
$38.00 Original price was: $38.00.$9.50Current price is: $9.50.
Complete Cloud Engineering Course In Linux
(0.0/ 0 Rating)
- 70 Lessons
- 66 Students
Intermediate
$38.00 Original price was: $38.00.$9.50Current price is: $9.50.
Complete Cloud Engineering Course In Linux
(0.0/ 0 Rating)
Unlock the full potential of Linux with our comprehensive course, "Complete Cloud Engineering Course In Linux": Server Management, Hosting, and...
- 70 Lessons
- 66 Students
Hi, Welcome back!


TECHNICAL Courses
Software Engineering
Software Engineering
Software engineering focuses on designing, building, testing, and maintaining software systems that solve real-world problems. It combines computer science principles with structured engineering practices to turn ideas into reliable applications, platforms, and tools used by millions of people every day.
A typical software engineering process involves understanding requirements, planning system architecture, writing and testing code, and continuously improving the software after release. This structured approach ensures that software is not only functional, but scalable, secure, and maintainable over time.
What does a Software Engineer do?
Software engineers design, develop, test, and maintain software applications and systems. Their work goes beyond writing code. They collaborate with designers, product managers, and other engineers to solve problems, improve performance, and fix bugs in both new and existing software.
Depending on interest and skill set, software engineers can specialize in areas such as front-end development, back-end development, full-stack development, mobile development, DevOps, systems design, or quality assurance. Each specialization plays a role in delivering stable and user-friendly software.
Why SE may be the right path for you
Software engineering may be a good fit if you enjoy problem-solving, structured thinking, and building things that work at scale. It suits people who like breaking complex problems into smaller parts and improving systems over time.
The field is highly collaborative and often requires working closely with others to bring a product to life. If you enjoy learning continuously, adapting to new tools, and contributing to team-based projects, software engineering offers a strong and flexible career path with long-term growth opportunities.



Data Science
Data Science
Software engineering focuses on designing, building, testing, and maintaining software systems that solve real-world problems. It combines computer science principles with structured engineering practices to turn ideas into reliable applications, platforms, and tools used by millions of people every day.
A typical software engineering process involves understanding requirements, planning system architecture, writing and testing code, and continuously improving the software after release. This structured approach ensures that software is not only functional, but scalable, secure, and maintainable over time.
What does a Data Scientist do?
Data scientists work with data throughout its lifecycle. Their responsibilities typically include cleaning and preparing data, exploring and visualizing datasets, building analytical or predictive models, and communicating findings to technical and non-technical stakeholders.
The broader data field includes several related roles such as data analyst, data engineer, data scientist, data architect, and machine learning engineer. While these roles differ in focus, they all contribute to turning raw data into usable insights and systems.
Why Data Science may be the right path for you
Data science may be a good fit if you enjoy working with numbers, patterns, and structured problem-solving. It suits people who are curious, analytical, and comfortable asking questions of data to uncover meaningful answers.
This path allows you to create impact by transforming data into insights that guide decisions and improve outcomes. If you enjoy combining logic, analysis, and real-world problem-solving, data science offers a challenging and rewarding career with strong demand across industries.




Cloud Engineering
Cloud Computing
Cloud engineering or cloud computing focuses on delivering computing resources such as servers, storage, databases, networking, and software over the internet. Instead of managing physical infrastructure, organizations use cloud platforms to build, scale, and operate applications more efficiently.
This approach allows teams to deploy products faster, scale resources as needed, and reduce the complexity of managing on-premise systems. Cloud computing now underpins most modern web and mobile applications.
What does a Cloud Professional do?
Cloud professionals design, deploy, and maintain cloud-based systems. Their work includes setting up cloud infrastructure, managing resources, ensuring system reliability, and implementing security best practices.
Common roles in this field include cloud engineer, cloud architect, DevOps engineer, and cloud consultant. While the specific responsibilities vary by role, all cloud professionals work to ensure that applications and services run securely, efficiently, and at scale.
Why Cloud Computing may be the right path for you
Cloud computing may be a good fit if you enjoy understanding how systems work together and solving infrastructure-related problems. It suits people who are comfortable learning new tools, adapting to changing technologies, and working across teams.
Strong problem-solving skills and a solid grasp of technical fundamentals are important in this field. If you are interested in building reliable systems behind the scenes and supporting applications used by many people, cloud computing offers a practical and in-demand career path.




Cyber Security
Cyber Security
Cyber security focuses on protecting computer systems, networks, applications, and data from digital threats. As organizations rely more on technology, the need to secure sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access has become a critical part of modern computing.
This field covers a wide range of threats, including malware, phishing attacks, data breaches, and system vulnerabilities. Cyber security professionals work to prevent attacks, detect risks early, and respond effectively when security incidents occur.
What does a Cyber Security professional do?
Cyber security professionals are responsible for securing systems and data across an organization. Their work includes monitoring networks, identifying vulnerabilities, implementing security controls, and responding to incidents that could compromise information or infrastructure.
Roles in this field include information security analyst, cyber security engineer, ethical hacker, security operations analyst, and information security manager. While responsibilities vary by role, the shared goal is to reduce risk and maintain the integrity of systems and data.
Why Cyber Security may be the right path for you
Cyber security may be a good fit if you are detail-oriented and enjoy identifying potential problems before they escalate. It suits people who think critically, enjoy investigating how systems can fail, and prefer working proactively to prevent issues.
This career path also requires continuous learning, as threats and security practices evolve constantly. If you enjoy protecting systems, responding to challenges in real time, and working in a role where your decisions directly impact safety and trust, cyber security offers a meaningful and in-demand career option.

Non Technical Courses
Pick A Non-Technical Course To Get Started
All Levels
$32.30 Original price was: $32.30.$9.50Current price is: $9.50.
Complete UI/UX Design Course for Beginners
(4.2/ 23 Ratings)
- 129 Lessons
- 1572 Students
All Levels
$32.30 Original price was: $32.30.$9.50Current price is: $9.50.
Complete UI/UX Design Course for Beginners
(4.2/ 23 Ratings)
Welcome to the UI/UX course! My name is Davio White, and I will be your instructor throughout this course. I...
- 129 Lessons
- 1572 Students
Beginner
$22.80 Original price was: $22.80.$11.40Current price is: $11.40.
Technical Writing Certification Course
(0.0/ 0 Rating)
- 63 Lessons
- 44 Students
Beginner
$22.80 Original price was: $22.80.$11.40Current price is: $11.40.
Technical Writing Certification Course
(0.0/ 0 Rating)
In this course, you will master the fundamentals of technical writing, a beginner’s guide to prepare you for monetizing your...
- 63 Lessons
- 44 Students
Beginner
$38.00 Original price was: $38.00.$7.60Current price is: $7.60.
Digital Marketing 101: Complete Course
(0.0/ 0 Rating)
- 35 Lessons
- 29 Students
Beginner
$38.00 Original price was: $38.00.$7.60Current price is: $7.60.
Digital Marketing 101: Complete Course
(0.0/ 0 Rating)
This Introductory guide to Digital Marketing is full of insights and strategy for business owners, marketing professionals, students, and anyone...
- 35 Lessons
- 29 Students
Beginner
$76.00 Original price was: $76.00.$11.40Current price is: $11.40.
Product Management Certification Course
(0.0/ 0 Rating)
- 50 Lessons
- 50 Students
Beginner
$76.00 Original price was: $76.00.$11.40Current price is: $11.40.
Product Management Certification Course
(0.0/ 0 Rating)
Product management is a discipline responsible for product planning (articulating the market problem) and product marketing (generating awareness, differentiation, and...
- 50 Lessons
- 50 Students



Product Design
UI/UX Design
UI and UX design focus on how people interact with digital products and how those interactions feel. UI design, which stands for User Interface Design, deals with the visual and interactive elements of a product, such as layout, colors, typography, and responsiveness. It focuses on how a product looks and how users interact with its interface.
UX design, or User Experience Design, takes a broader view. It focuses on the overall experience a user has with a product, from how intuitive it is to use to how efficiently users can complete tasks. UX design considers usability, accessibility, and user satisfaction across the entire journey.
Together, UI and UX design ensure that digital products are not only visually appealing but also practical, easy to use, and enjoyable.
What do UI/UX Designers do?
UI designers are responsible for designing clear, visually consistent interfaces that align with a brand and guide users smoothly through a product. Their work includes designing layouts, selecting colors and typography, creating responsive designs, and refining visual details that improve usability.
UX designers focus on understanding users and designing experiences around their needs. They conduct user research, define user personas, structure information, create wireframes and prototypes, and test designs to ensure products are functional and intuitive. UX designers work closely with UI designers, product managers, and engineers to refine the overall experience.
Why UI/UX Design may be the right path for you
UI/UX design may be a good fit if you are creative and enjoy solving problems through design. It suits people who are interested in how users think, how products are experienced, and how design decisions impact usability.
This path involves strong collaboration with cross-functional teams and requires curiosity, attention to detail, and continuous learning. If you enjoy combining creativity with analytical thinking and want to shape how people experience technology, UI/UX design offers a rewarding career within the tech industry.




Project Management
Project Management
Project management focuses on planning, organizing, and overseeing work to ensure projects are completed efficiently and successfully. It involves coordinating people, timelines, resources, and processes to move a project from initiation to completion while meeting defined goals.
In tech and digital teams, project management plays a critical role in ensuring that ideas are executed smoothly, deadlines are met, and teams stay aligned throughout the project lifecycle.
What does a Project Manager do?
Project managers define project objectives, create plans, and coordinate teams to ensure work progresses as expected. They are responsible for setting timelines, allocating resources, tracking progress, and addressing issues that may affect delivery.
They also act as a central point of communication between stakeholders, ensuring that expectations are clear and that everyone involved understands their role. A key part of the role is identifying risks early and adjusting plans to keep projects on track.
Why Project Management may be the right path for you
Project management may be a good fit if you are organized, communicative, and comfortable leading teams toward shared goals. It suits people who enjoy planning, coordinating tasks, and helping others work effectively together.
Strong problem-solving skills, attention to detail, and the ability to manage time and priorities are essential in this role. If you enjoy bringing structure to complex work and ensuring projects are delivered successfully, project management offers a practical and impactful career path within tech and beyond.




Product Management
Product Management
Product management focuses on guiding a product throughout its lifecycle, from idea and development to launch and continuous improvement. The role sits at the intersection of business, technology, and user needs, ensuring that products deliver real value to customers while supporting organizational goals.
In tech, product management helps teams decide what to build, why it should be built, and how success will be measured.
What does a Product Manager do?
Product managers identify user problems and business opportunities, define product goals, and translate those goals into clear requirements for technical and design teams. They work closely with engineers, designers, and stakeholders to prioritize features, align on direction, and ensure products are built with purpose.
They are also responsible for communicating product vision, gathering feedback, and making informed decisions based on user insights, data, and business constraints.
Why Product Management may be the right path for you
Product management may be a good fit if you enjoy understanding how people use products and thinking about how to improve those experiences. It suits individuals who are curious, analytical, and comfortable making decisions in complex environments.
This path requires strong communication, problem-solving, and collaboration skills. If you enjoy shaping ideas into real products, balancing user needs with business goals, and working closely with cross-functional teams, product management offers a challenging and impactful career option.



Technical Writing
Technical Writing
Technical writing focuses on explaining complex technical information in a clear and structured way. It involves creating documentation that helps users, developers, or stakeholders understand how a product, system, or process works.
In the tech industry, technical writing plays a key role in making software, tools, and services usable. Clear documentation reduces confusion, improves adoption, and supports both technical and non-technical audiences.
What does a Technical Writer do?
Technical writers create and maintain documentation such as user guides, product documentation, API references, tutorials, and internal knowledge bases. Their work involves gathering information from subject matter experts, organizing content logically, and translating technical details into clear, accessible language.
They also review and update documentation to ensure accuracy as products evolve. Technical writers often collaborate closely with engineers, product managers, and support teams.
Why Technical Writing may be the right path for you
Technical writing may be a good fit if you enjoy writing, explaining ideas, and paying attention to detail. It suits people who are comfortable learning technical concepts but prefer communication over coding.
This path allows you to work in tech without being an engineer while still contributing directly to product quality and user understanding. If you enjoy clarity, structure, and helping others learn through documentation, technical writing offers a strong and flexible career option.




Product and Digital Marketing
Product, Digital Marketing, and Tech Sales
Product, digital marketing, and tech sales focus on how technology products reach users, gain adoption, and generate revenue. These roles sit at the intersection of technology, business, and customer needs, ensuring that products are positioned correctly, communicated clearly, and sold effectively.
In tech companies, growth depends not only on building good products, but also on how well those products are marketed, explained, and sold to the right audience.
What Do They All Do?
Product marketers define how a product is positioned in the market. They research customers, shape messaging, support product launches, and work closely with product teams to communicate value clearly.
Digital marketers focus on reaching and engaging users through online channels such as search engines, content, email, and social platforms. They run campaigns, analyze performance data, and continuously optimize strategies to drive awareness and adoption.
Tech sales professionals focus on building relationships with potential customers and helping them understand how a product solves their problems. Their work includes lead qualification, product demonstrations, handling objections, and closing deals, often in collaboration with marketing and product teams.
Why Any of These Roles May Be The Right Path For You
This path may be a good fit if you enjoy communication, persuasion, and understanding customer behavior. It suits people who are comfortable explaining ideas, building relationships, and working toward measurable outcomes such as growth or revenue.
Strong listening skills, curiosity, and adaptability are important across all three roles. If you enjoy influencing decisions, working with people, and contributing directly to how a product succeeds in the market, product marketing, digital marketing, or tech sales offer practical and rewarding career options in tech.




Tech Support
Tech Support
Tech support focuses on helping users resolve technical issues and use technology products effectively. It plays a critical role in ensuring that software, hardware, and digital services function as intended for customers and internal teams.
In tech companies, support teams act as the bridge between users and technical teams, identifying recurring problems, improving product reliability, and protecting user trust through timely and accurate assistance.
What does a Tech Support professional do?
Tech support professionals assist users by diagnosing and resolving technical issues related to software, systems, or devices. Their responsibilities often include responding to support requests, troubleshooting errors, guiding users through solutions, and documenting common issues.
They also escalate complex problems to engineering teams and provide feedback that helps improve products. Depending on the organization, roles may include technical support specialist, customer support engineer, IT support analyst, or service desk analyst.
Why Tech Support may be the right path for you
Tech support may be a good fit if you enjoy helping people and solving problems in a practical, hands-on way. It suits individuals who are patient, detail-oriented, and comfortable communicating with both technical and non-technical users.
This role is often a strong entry point into tech, offering exposure to real systems, products, and workflows. If you are interested in learning how technology works while building experience and confidence, tech support can be a valuable starting point with opportunities to grow into more specialized roles.

Finally
Choosing the Right Tech Path
There is no single correct way to start a career in tech. Some people begin with technical roles, others start in non-technical positions, and many transition between paths over time. The most important step is choosing a direction that aligns with your interests, strengths, and willingness to learn.
Starting Small and Building Consistently
Breaking into tech does not require knowing everything at once. Progress comes from learning the fundamentals, practicing consistently, and gaining real-world exposure through projects, training, or entry-level roles. Small, focused steps compound over time.
Moving Forward with Clarity
Once you understand the available paths, the next step is taking action. Whether you choose to learn a technical skill, explore a non-technical role, or build transferable skills, clarity and commitment matter more than speed. With the right guidance and structure, starting a tech career becomes achievable.