Currently Empty: $0.00
aptLearn
The Importance of User Experience (UX) in Product Development
User Experience (UX) is not just a buzzword. It’s a crucial part of product development that can make or break your product’s success. But what exactly is UX? And why is it so important? This comprehensive guide explores the various stages of the UX process and delves into additional topics related to UX in product development. From understanding the user to continuous improvement, we will explore each stage and highlight best practices to create exceptional user experiences. Let’s dive in and explore.
What is User Experience (UX)?
At its core, User Experience is all about how a user interacts with, feels about, and uses your product. It’s about creating a product that’s not just functional and reliable but also enjoyable to use.
UX is not just about the user interface (UI); it’s about the entire journey a user takes from the moment they discover your product, through the process of using it, and even beyond. It’s about understanding your users’ needs, wants, and even their pain points, and then designing a product that not only meets but exceeds their expectations.
Why is UX Important in Product Development?
Now that we understand what UX is let’s talk about why it’s so important in product development.
- Firstly, a great UX can lead to increased user satisfaction, which can result in higher user retention rates. When users enjoy using your product, they’re more likely to continue using it and even recommend it to others.
- Secondly, investing in UX can save you money in the long run. By understanding your users’ needs and testing your product early and often, you can identify and fix any issues before they become costly problems.
- Finally, a well-designed product that meets users’ needs can set you apart from your competitors. In today’s competitive market, a great UX can be your key to standing out and gaining a competitive edge.
The UX Process in Product Development
Now, let’s walk through the typical UX process in product development. This process can vary depending on the project and the team, but it generally includes the following stages:
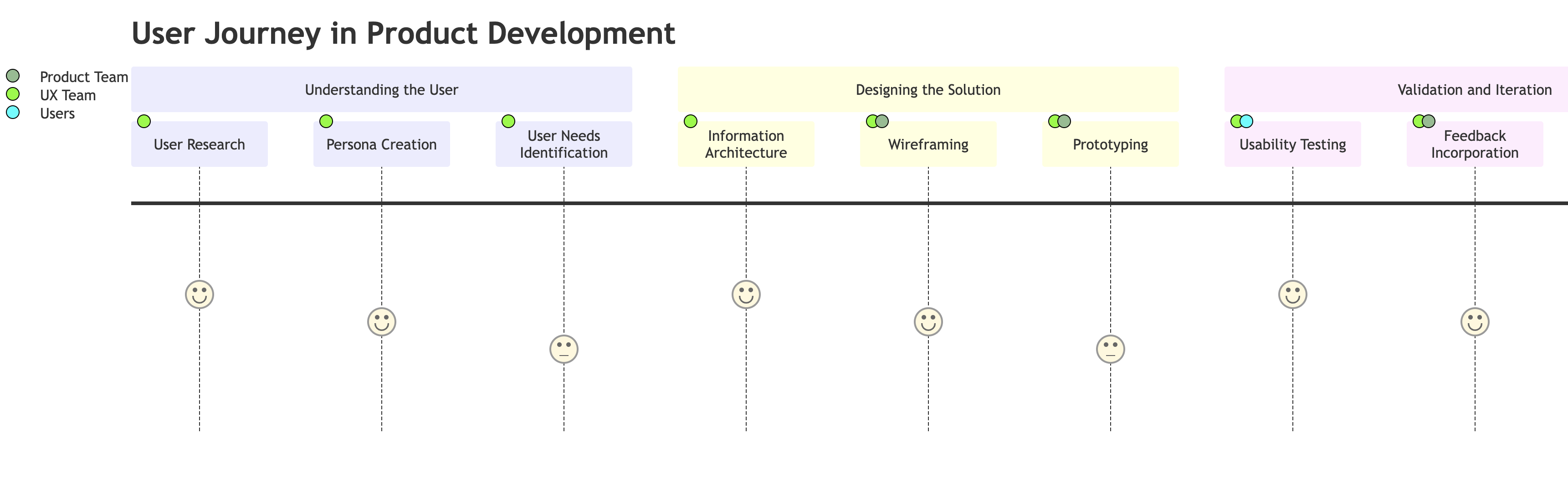
Understanding the User
- User Research: This is where it all begins. User research is all about understanding who your users are, what they need, what they value, and how they behave. This can involve methods like surveys, interviews, and user testing. The goal here is to gather as much information as possible about your users to inform your design decisions. To build a product that resonates with users, it is crucial to conduct user research. This understanding forms the foundation for creating user-centric products.
- Persona Creation: Once you’ve conducted your user research, you can create personas. Personas are fictional representations of user groups. By creating well-defined personas, you can better empathize with your target audience and tailor your product to meet their specific needs. This section provides guidance on creating personas and leveraging them in the design process. They help you understand your users’ needs, experiences, behaviours, and goals.
- User Needs Identification: Now that you have your personas, you can identify their needs. This involves understanding what your users need from your product and what problems your product can solve for them. Understanding and prioritizing user needs is key to delivering a successful product.
Designing the Solution
- Information Architecture: This involves organizing and structuring the information in your product. A well-structured information architecture and intuitive user flow are essential for a seamless UX. Here is where we explore how to design information hierarchies and create user flows that guide users effortlessly through the product, and thereby ensuring a satisfying experience. It’s all about making sure that information is presented in a way that’s understandable and easy for your users to navigate.
- Wireframing: Before diving into development, wireframes and prototypes serve as valuable tools for visualizing and testing the product design. Wireframes are like the blueprints of the product. They provide an illustrated guide to the structure and layout of your product without any design elements like colours or typography.
- Prototyping: Prototypes are interactive versions of your wireframes. Key design principles, including simplicity, consistency, and usability, serve as guiding beacons for UX designers. They allow you to test your design and get feedback from users before you start development.
Validation and Iteration
- Usability Testing: This is where you test your prototype with real users by employing various usability testing methods, such as moderated user testing or remote usability testing; you can identify pain points and areas for improvement in your product’s design.
- Feedback Incorporation: After testing, you’ll likely have a list of things to improve. This is where you incorporate that feedback and make changes to your design.
- Iterative Design: UX design is an iterative process. We can also call this A/B testing; this allows you to compare and validate design decisions by testing alternative versions of a feature or interface. Discover how this data-driven approach can guide design choices and optimize the user experience. This means you’ll likely go through multiple rounds of design, testing, and refinement.
Launch and Beyond
- Product Launch: After all the testing and refinements, it’s time to launch your product. But the UX process doesn’t end here.
- User Feedback Collection: After launch, it’s important to continue collecting user feedback. This can help you understand how users are interacting with your product in the real world and identify any areas for improvement.
- Continuous Improvement: Based on the feedback, you’ll continue to make improvements and updates to your product. The UX process is a cycle of continuous learning and improvement.
The UX Process Class
Now that we have a high-level overview of the process let’s take a closer look at the roles involved in the UX process and the responsibilities associated with each role.
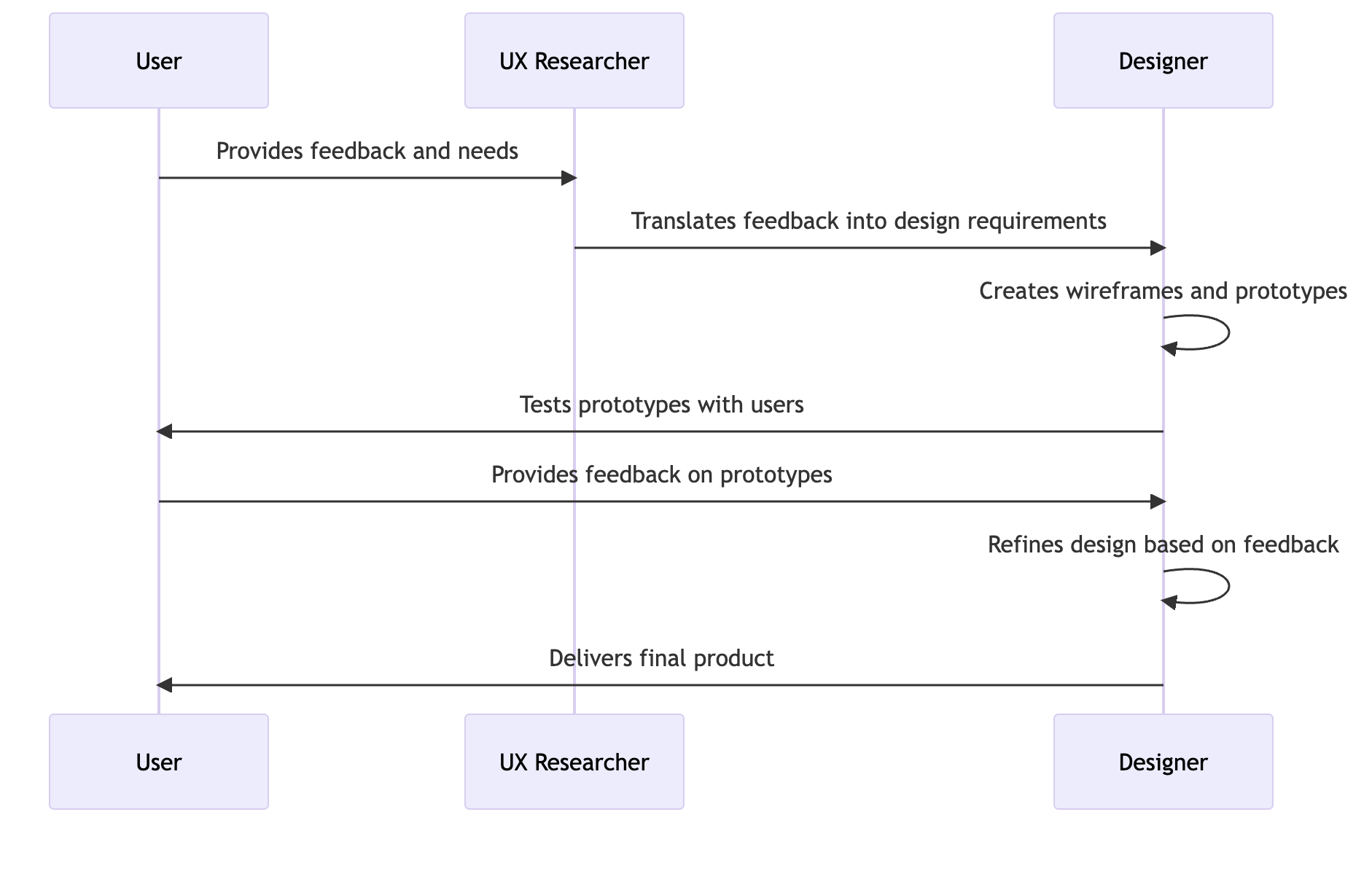
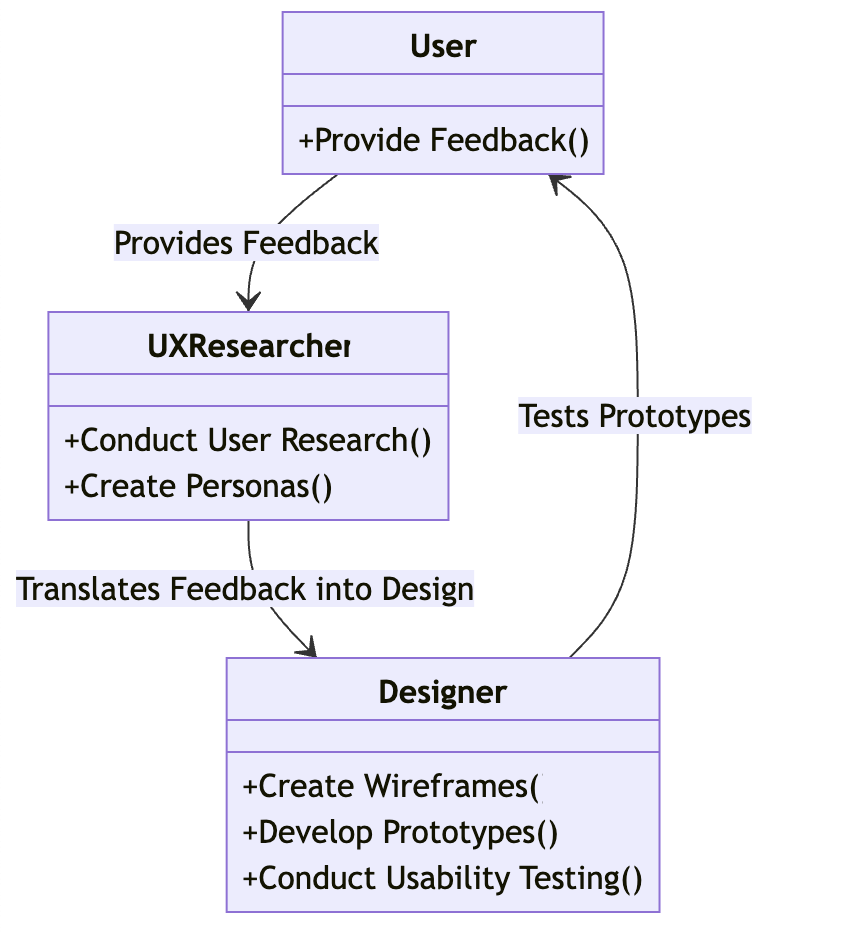
In the UX process, the user, the UX researcher, and the designer each play a crucial role. The user is the one who uses the product and provides feedback. The UX researcher conducts user research and creates personas to better understand the user’s needs and behaviours. The designer then takes these insights and translates them into the design of the product. They create wireframes, develop prototypes, and conduct usability testing to ensure that the product meets the user’s needs and provides a good user experience.
Today prioritizing UX in product development is a necessity. By understanding the user, designing intuitive solutions, validating through testing and feedback, and continuously improving the product, organizations can create compelling user experiences that drive customer satisfaction and business success, read EchoVaults story. By incorporating the additional topics covered, such as accessibility, mobile UX, Agile development, and UX metrics, you can ensure a comprehensive approach to UX design that elevates your products above the rest. Embrace the power of UX and embark on a journey to deliver exceptional experiences for your users. UX is not just a nice-to-have in product development; it’s a must-have. It’s a crucial part of creating a product that not only meets users’ needs but also provides a delightful and seamless experience. So, the next time you’re working on a product, remember to keep your users at the heart of your design process. After all, a happy user leads to a successful product.
Recommendations
As we’ve explored in this article, User Experience (UX) plays a crucial role in product development. It’s a field that’s not just about creating aesthetically pleasing designs but about understanding users’ needs and creating products that provide a seamless and enjoyable user experience.
If you’re interested in diving deeper into this fascinating field, we highly recommend taking the UI/UX Design Course for All Levels offered by aptLearn. This course is designed to equip you with the skills and knowledge you need to excel in UX design, regardless of your current level of expertise.
In addition, if you’re interested in the broader field of product management, we also recommend the Free Product Management Certification course. This course will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the product management process, including UX design, product strategy, and project management.
By taking these courses, you’ll not only gain valuable skills and knowledge, but you’ll also be positioning yourself for success in the rapidly evolving tech industry. Whether you’re a beginner looking to break into the field, or an experienced professional looking to upskill, these courses are a fantastic resource. So why wait? Start your learning journey with aptLearn today and take the first step towards a rewarding career in UX design and product management.